Revolution Medicines’ Clinical Trial Program Is Evaluating Investigational Treatments for RAS Mutant Cancers
Our novel RAS(ON) inhibitors are under investigation for treating different types of RAS mutant cancers, including pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), colorectal cancer (CRC), and other solid tumors
Revolution Medicines’ RAS(ON) Inhibitor Clinical Trials Program
explore more trials
Daraxonrasib
Elironrasib
Zoldonrasib
RAS(ON) inhibitor combinations
RASolute 304
(Phase 3)
Resected PDAC
RASolve 301
(Phase 3)
Previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic RAS mutant NSCLC
RASolute 302
(Phase 3)
Previously treated metastatic PDAC
RMC-6236-001
(Phase 1/2)
Treatment naïve or previously treated advanced solid tumors haboring specific mutations in RAS
RMC-6291-001
(Phase 1/1b)
Locally advanced or metastatic KRAS G12C mutant solid tumors
RMC-9805-001
(Phase 1/1b)
Previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic KRAS G12D mutant solid tumors
RMC-LUNG-101
(Phase 1b/2)
Locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC or other advanced solid tumors
RMC-GI-102
(Phase 1/2)
Previously treated and treatment-naïve solid tumors, particularly gastrointestinal tumors
RMC-6291-101
(Phase 1b)
Previously treated advanced or metastatic KRAS G12C mutant solid tumors
Daraxonrasib
RASolute 302
(Phase 3)
Previously treated metastatic PDAC
RASolute 304
(Phase 3)
Resected PDAC
RASolve 301
(Phase 3)
Previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic RAS mutant NSCLC
RMC-6236-001
(Phase 1/2)
Treatment naïve or previously treated advanced solid tumors haboring specific mutations in RAS
Elironrasib
RMC-6291-001
(Phase 1/1b)
Locally advanced or metastatic KRAS G12C mutant solid tumors
Zoldonrasib
RMC-9805-001
(Phase 1/1b)
Previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic KRAS G12D mutant solid tumors
RAS(ON) inhibitor combinations
RMC-GI-102
(Phase 1/2)
Previously treated and treatment-naïve solid tumors, particularly gastrointestinal tumors
RMC-LUNG-101
(Phase 1b/2)
Locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC or other advanced solid tumors
RMC-6291-101
(Phase 1b)
Previously treated advanced or metastatic KRAS G12C mutant solid tumors
The safety and efficacy of the agents and/or uses under investigation have not been established
aThis is not a complete list of eligibility criteria; for more information, please go to ClinicalTrials.gov. bThese criteria are for specific subprotocols within the clinical trial. Refer to the ClinicalTrials.gov record for more information.
RAS Protein Biology and RAS Mutant Cancers
RAS Proteins Play a Key Regulatory Role in Cell Growth and Development
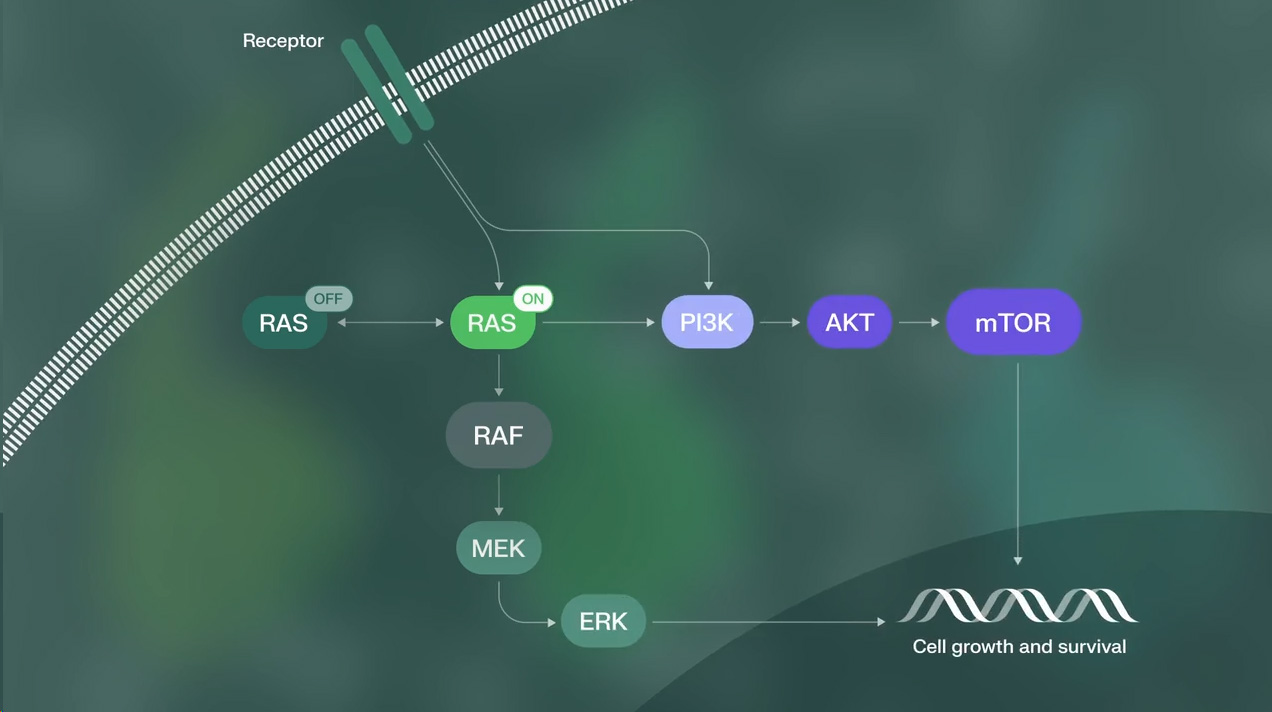
This visual is for illustrative purposes only and does not represent all molecular components
of the RAS pathway.
RAS Mutations Are Common Across Multiple Tumor Types and Are Associated With Poor Survival Outcomes
RAS mutations

- RAS mutations are present in approximately one-fifth of human cancers
- In the presence of oncogenic mutations, such as G12X,a G13X,a and Q61X,a RAS proteins (i.e., KRAS, HRAS, or NRAS) are predominantly ON, which can drive cancer initiation and progression
RAS mutations in cancers

- Cancers commonly driven by RAS mutations include PDAC (~92% RAS mutant), CRC (~50% RAS mutant), and NSCLC (~30% RAS mutant), all of which exhibit a wide array of RAS variants
- Inhibiting RAS signaling could impede tumor growth, but there are limited therapeutic options that directly inhibit RAS
This visual is for illustrative purposes only and represents a high-level depiction of select RAS mutations.a
a“X” denotes any amino acid residue point mutation in a given codon (i.e., G12C, G12D, G12V, G13D, Q61H).
Please click on the pancreas, colon, or lungs to learn more about each disease state
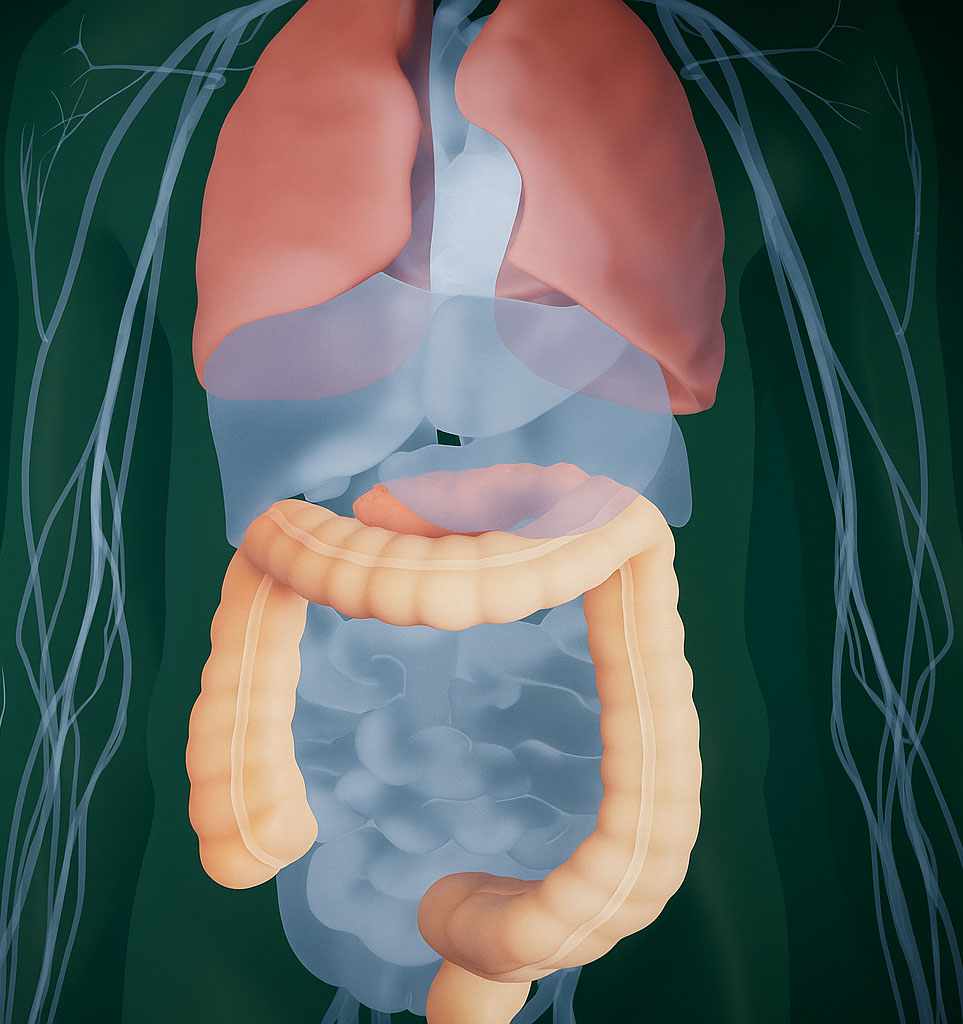
Please click on the pancreas, colon, or lungs to learn more about each disease state

The Tri-Complex Inhibitor Platform
RAS(ON) Tri-Complex Inhibitors Are Designed to Block RAS(ON) Activity
Click on the different components to see how RAS(ON) tri-complex inhibitors work
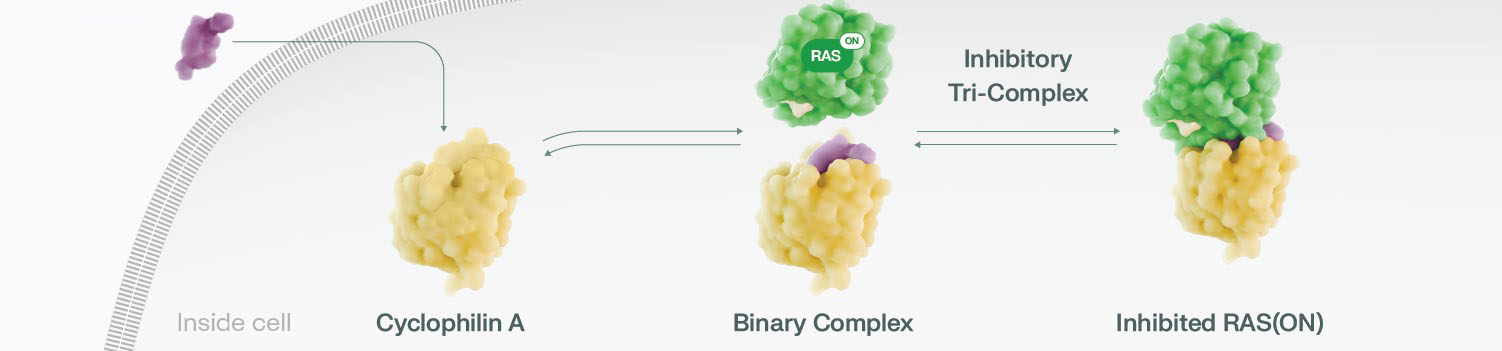
Click on the different components to see how RAS(ON) tri-complex inhibitors work
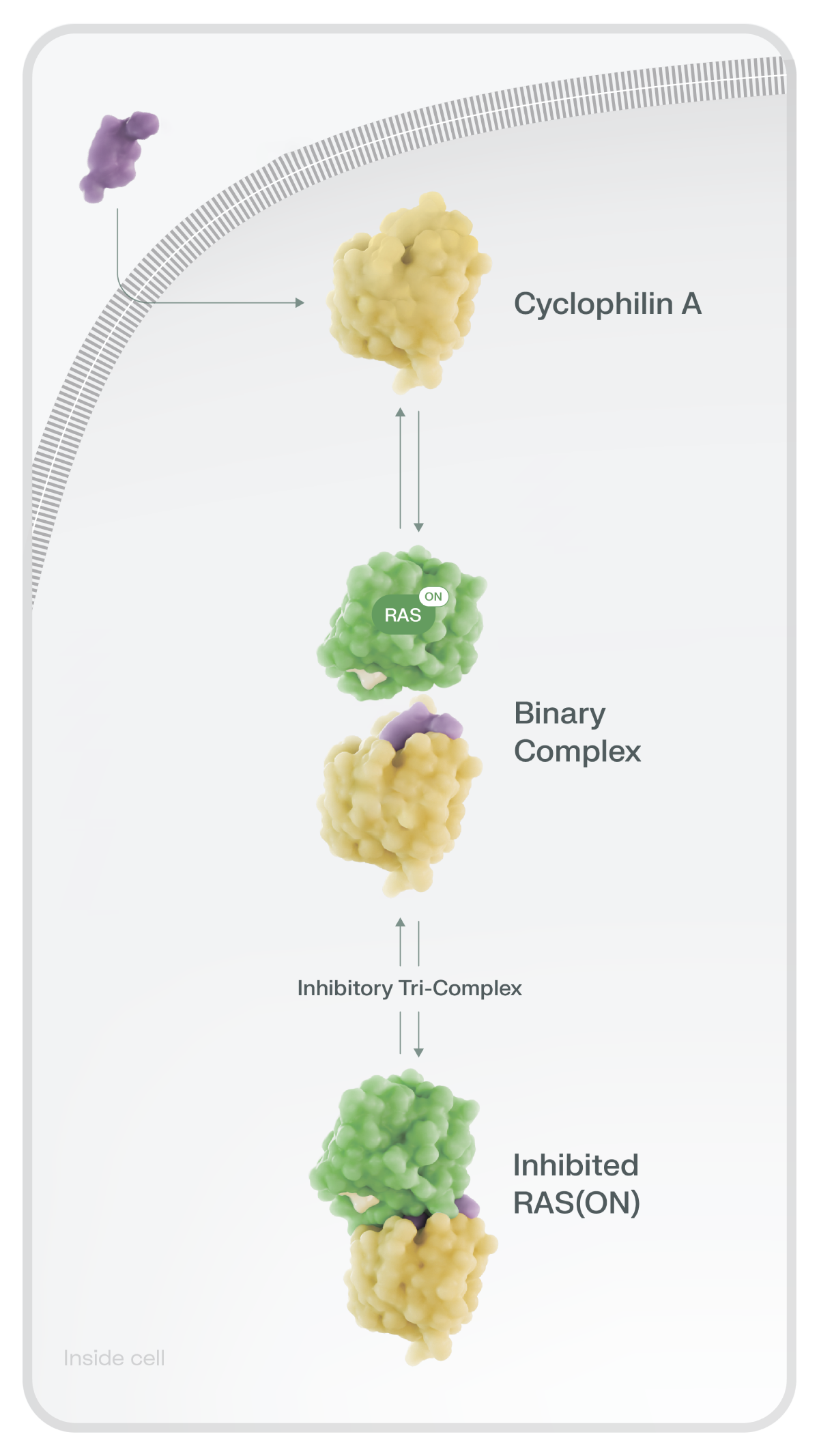
Revolution Medicines’ novel tri-complex inhibitor platform is intended to block RAS in its ON state
and reduce downstream oncogenic signaling
Investigational RAS(ON) Inhibitors
Three Investigational Revolution Medicines RAS(ON) Inhibitors Are in Clinical-Stage Trials for Treating RAS Mutant Cancers
Daraxonrasib (RMC-6236)
A RAS(ON) multi-selective
noncovalent inhibitor

Ongoing clinical trials in PDAC and NSCLC
Current Phase 3 or early phase clinical trials include RASolute 302, RASolve 301, and RMC‑6236‑001
Zoldonrasib (RMC-9805)
A RAS(ON) G12D-selective
covalent inhibitor

Ongoing clinical trials in advanced solid tumors
Current early phase clinical trials include RMC‑LUNG‑101, RMC‑9805‑001, and RMC‑GI‑102
Elironrasib (RMC-6291)
A RAS(ON) G12C-selective
covalent inhibitor

Ongoing clinical trials in advanced solid tumors
Current early phase clinical trials include RMC‑LUNG‑101, RMC‑6291‑101, and RMC‑6291‑001
Click here for more information about Revolution Medicines’ RAS(ON) inhibitor pipeline
